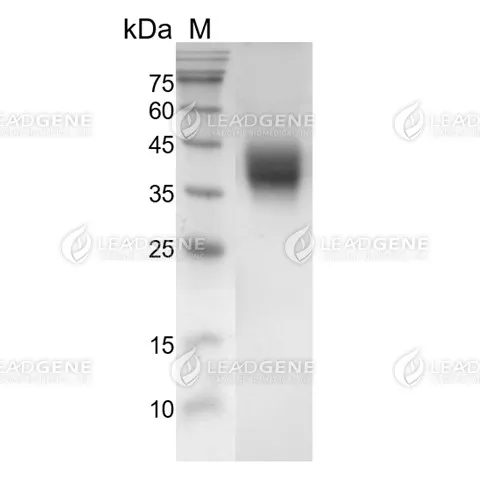
Description
PD-L1 regulates immune responses by binding to the immunoinhibitory receptor PD-1 on activated T-cells and B-cells. This interaction can suppress T-cell responses by inducing apoptosis and arresting cell-cycle progression. In cancer, PD-L1's role in reducing antigen-specific T cells can promote tumor growth and immune evasion. As a result, PD-L1 is considered as a potential therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases and cancer.