Recombinant protein expression is a biotechnological platform to generate a protein of interest by transmitting an exogeneous gene expression plasmid into a production cell factory, and through a series of culturing, harvesting, purifying and sometimes refolding process, the target protein is finally obtained. Generally, mammalian (CHO-S and HEK293), insect (Sf9) and yeast (X-33) cell lines belonging to the eukaryotic expression system can perform better folding and secretion activities in synthesizing proteins. Whereas, the prokaryotic system that usually means Escherichia coli B strain cells provides a rapid and more affordable choice. Below we briefly introduce these expression systems.
|
Prokaryotic expression system |
E.coli cells are easy to operate. They can be conveniently transformed and grow fast in relatively cheap broths, thus making this microorganism a popular choice to produce lots of recombinant proteins in a short period of time. However, defects that the overexpressed proteins are often precipitated as inclusion body which is difficulty to solve and limited post translational modification (PTM) activity.
There are several factors may affect the yield of E. coli:
- Gene (codon) optimization:
According to the choice of the expression vector and expression host system, it is necessary to replace the codons and adjust the GC content in the sequence of target gene. - Vector selection:
High copy numbers and highly activated promoters are selected as expression vectors including pET, pGEX and pQE vector。
After a few hours of induction, the target protein can express more than 50% of the total protein in the host. - Host selection:
-BL-21:Lack of endogenous protease ompT, ompP and Lon protease, the target protein can be prevented to degrade.
-BL21 (DE3):The chromosome of DE3 contains T7 polymerase to drive the expression of foreign target proteins.
-Rosetta:After modification, it can improve the efficiency of eukaryotic gene expression.
|
Eukaryote- Mammalian cells |
Mammalian cells have complete post-translational modification (PTM), disulfide bond formation and correct protein folding. Generally, the most commonly used mammalian cells for recombinant proteins expression are HEK293, CHO and NS0 cells. The mammalian cell expression system will also be used to product secreted proteins and recombinant antibodies. The expressed proteins or antibodies can be collected from the cell culture medium to perform the next purification steps.
|
Eukaryote-Yeast / Pichia pastoris |
Yeasts are lower single-celled eukaryote. It has partial post-translational modification (PTM) of proteins. The proteins folding is also more correct than that of E. coli, and it has the ability to form disulfide bonds. Yeast can be used to produce recombinant proteins on a large scale, which can reduce production costs.
|
Baculovirus-infected insect cells |
Insect cells have extensive post-translational modification of proteins like mammalian cells. Generally, Spodoptera frugiperda, sf9 or sf21 cells, are most commonly used for recombinant proteins expression. To amplify the target proteins, insect cells are infected by baculovirus. The insect cells are suitable for high-density suspension culture and also for secreted protein expression.
Table . Features of commonly used protein expression systems.
|
||||||||||||||||||
Abbreviations: PTMs (post-translational modifications)
|
The application of recombinant proteins |
Recombinant proteins can be used to study gene regulation, and the recombinant proteins are widely used, including:
- Production of antibodies
- Structural analysis
- Cell therapy
- Activity analysis
- Drug development
- Vaccine improvement and development
- Diagnostic reagents or kits
- Animal experiment
- Cell experiment
- Raw materials for skin care products
|
Our Advantages |
We offer a wide range of premium recombinant proteins to support scientific research. Our protein products have expanded to include a wide range of cytokines, neurotrophins, chemokines, growth factors, and many more. Our recombinant proteins are animal-free and undergo multiple quality checks, ensuring that each product contains a purity over 95%, contains a low endotoxin level (<0.1 EU per μg), and maintains a high biological activity.
- Stable expression
- Antibiotic-free
- Animal-free
- Abundant expression experience
-
Optimize the lyophilization of proteins, which has more advantages in storage.
-
Quality assurance
At present, more than 500 different species of recombinant proteins have been successfully expressed, including humans, mice, swine, etc. The success rate of protein expression reaches 90%. These recombinant proteins have been successfully used in antibody preparation, antibody drug development, diagnostic reagents (ELISA kit and Lateral flow test), vaccine research, and so on.
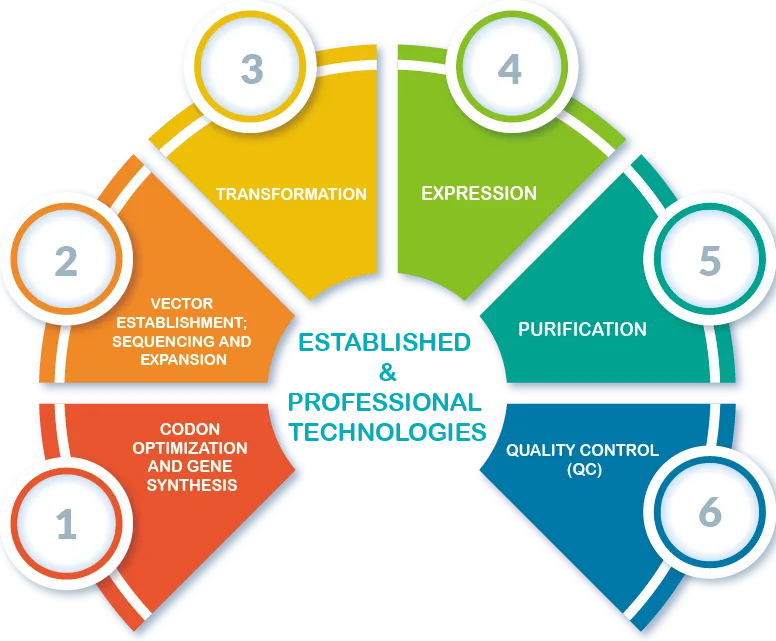
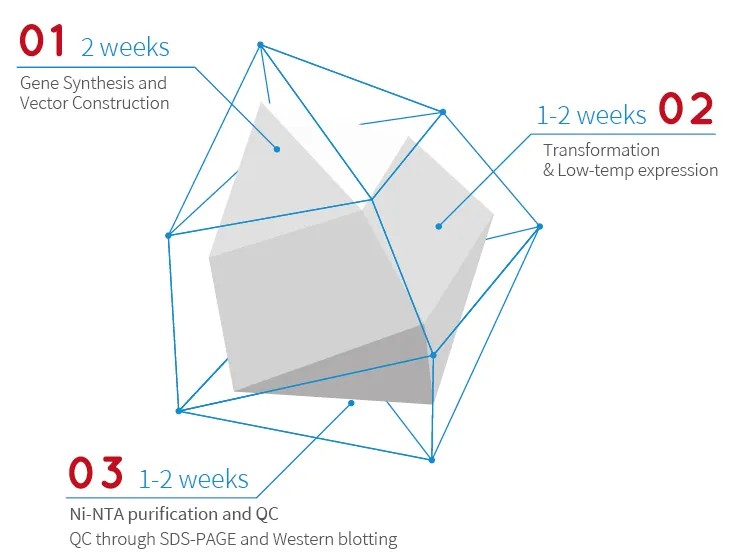
|
Our Quality |
- High purify
->98% by HPLC evaluation
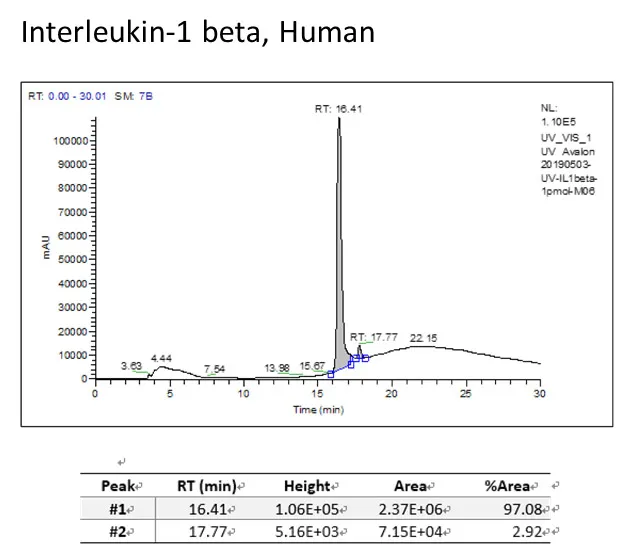
- Biological activity
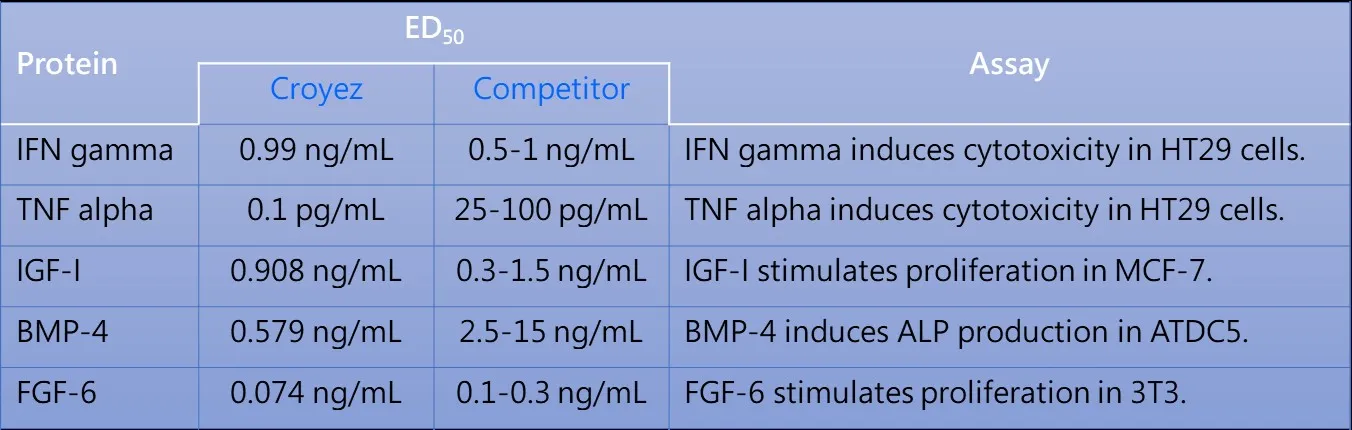
- Low endotoxin
- <0.1 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method
|
The application of recombinant proteins |
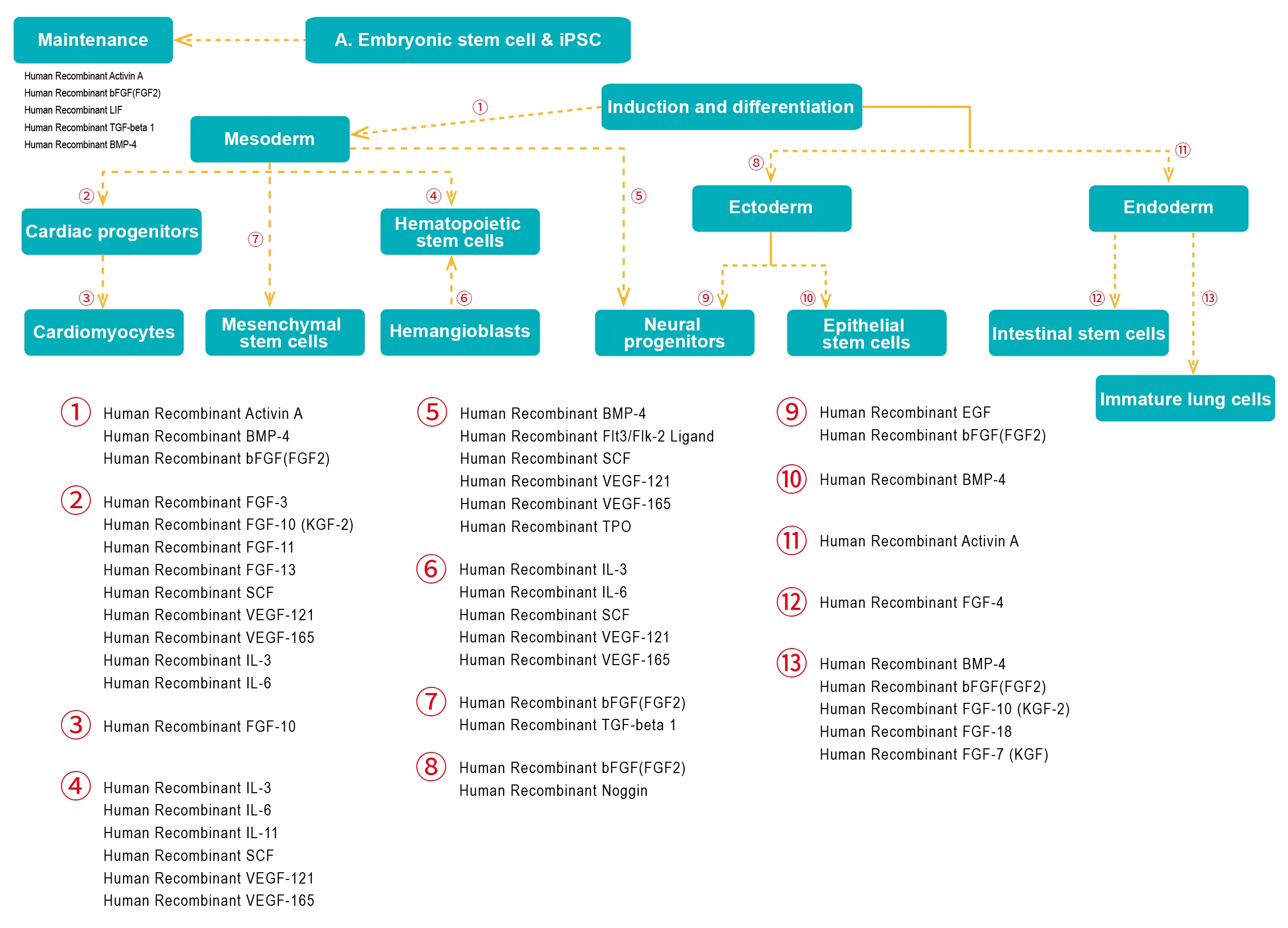
- Embryonic stem cell & iPSC
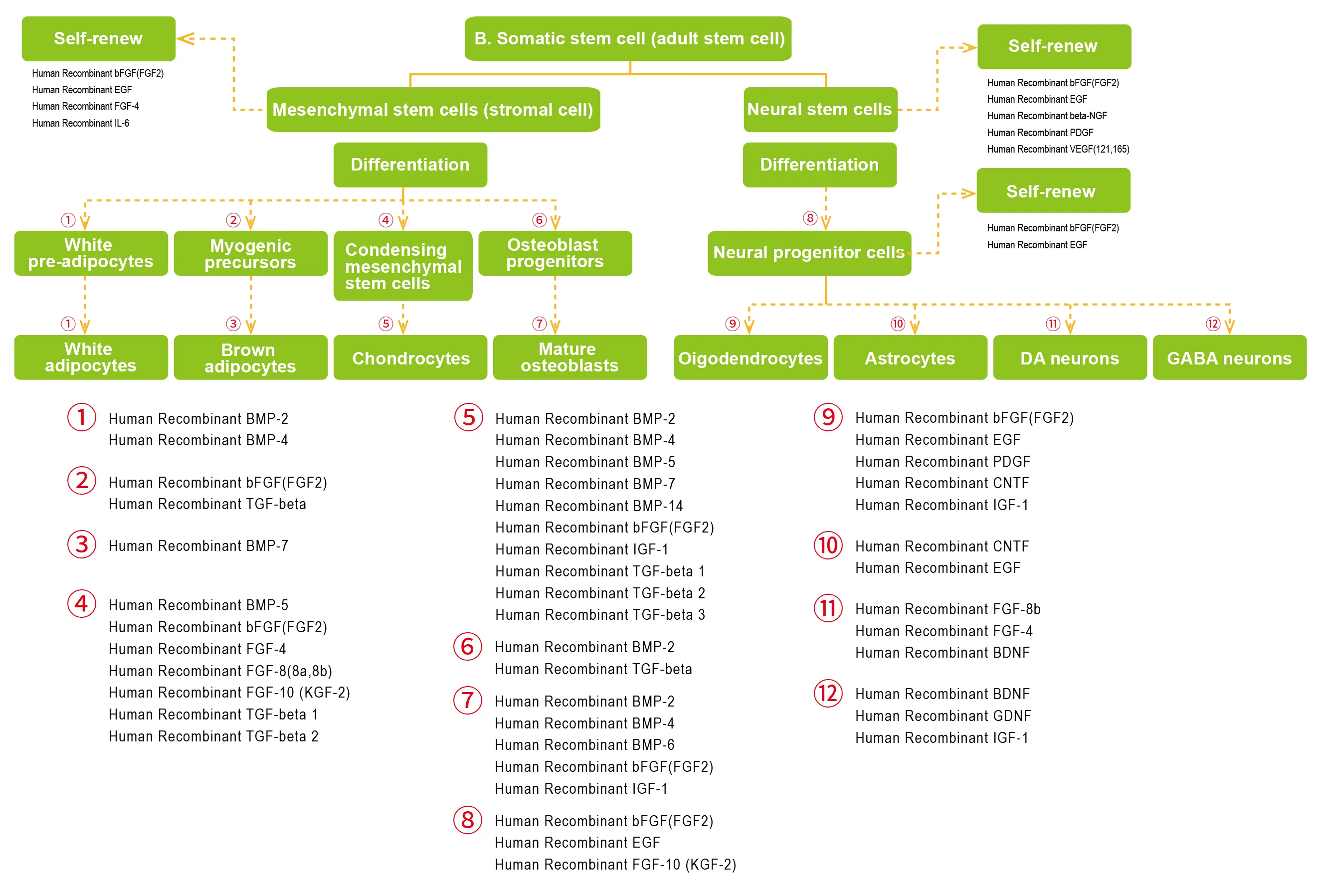
- Somatic stem cell (adult stem cell)
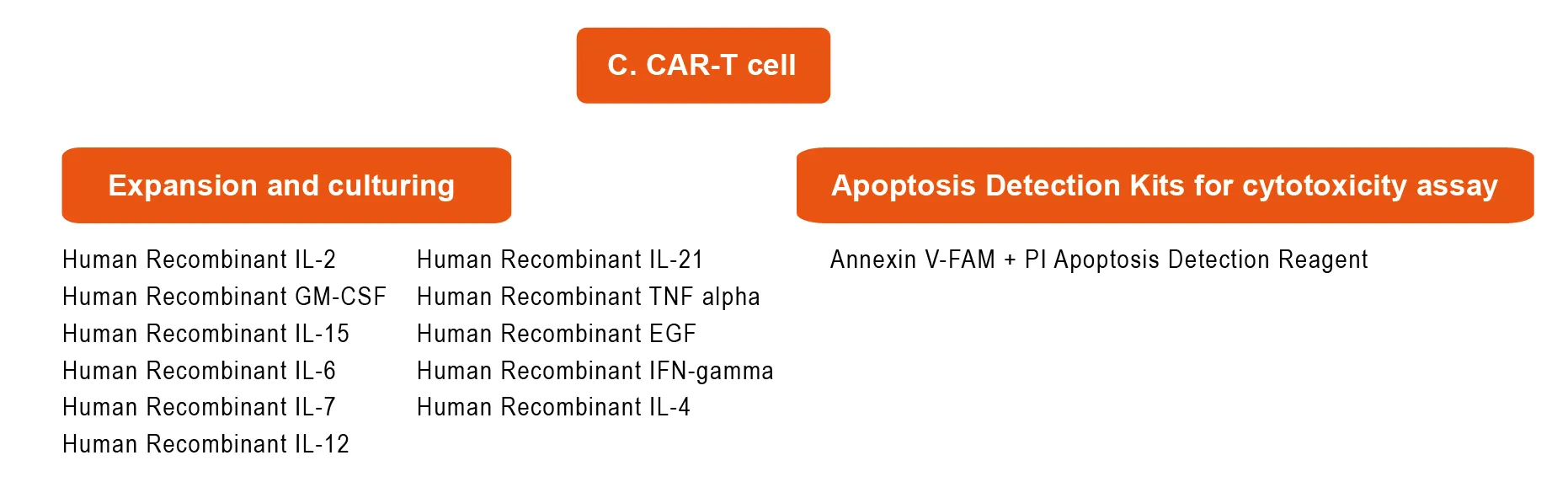
- CAR-T cell
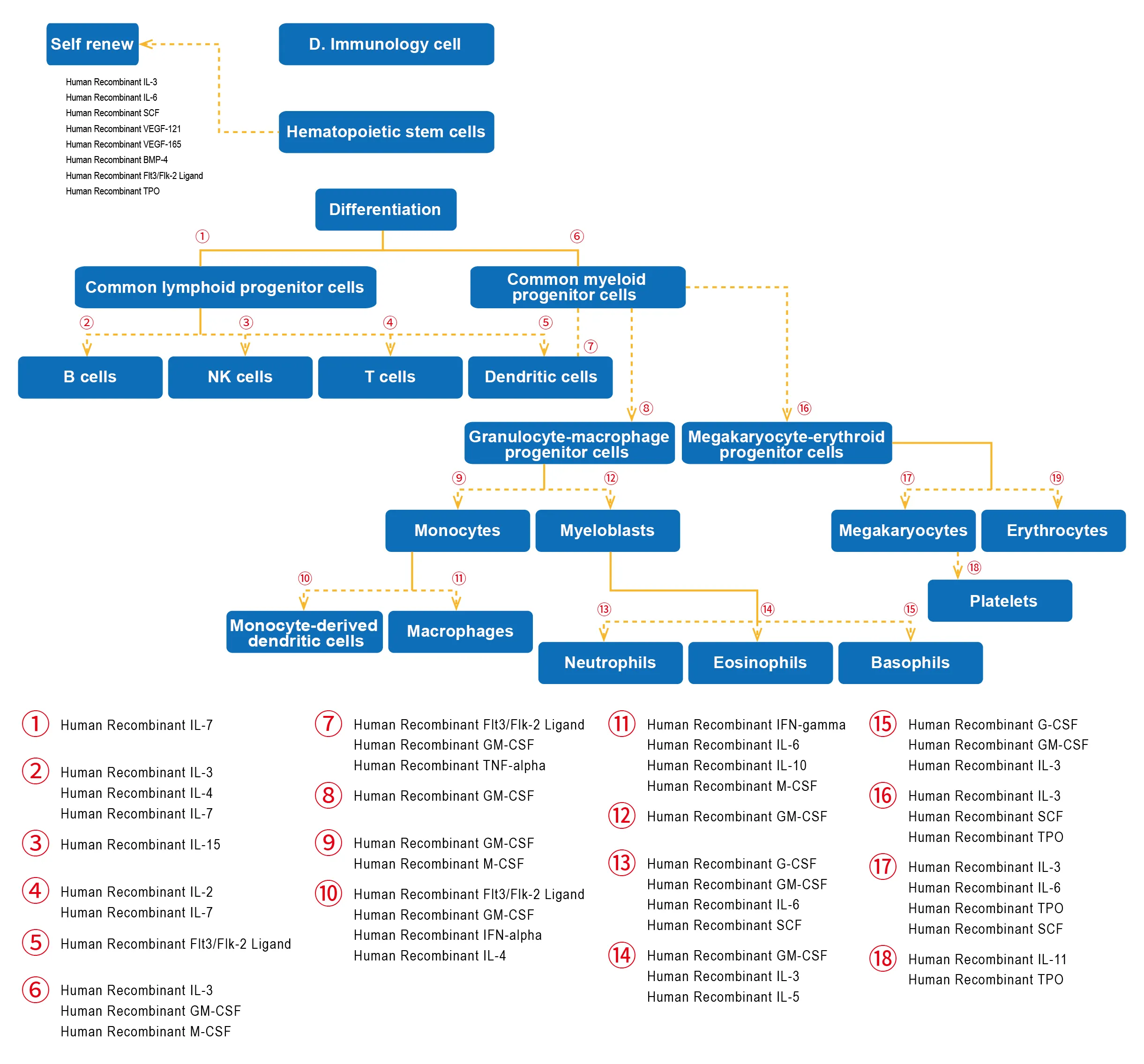
- Immunology cell